Introduction to Mosquito Diseases
Overview of Mosquito-borne Illnesses
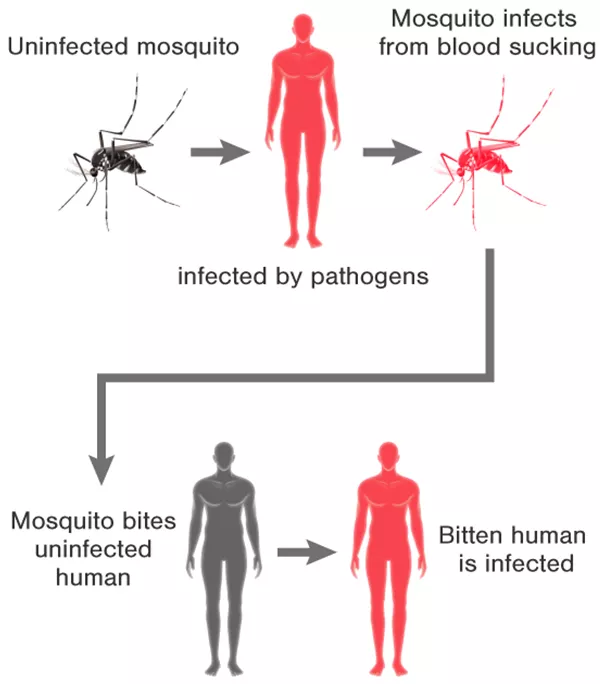
Mosquito-borne illnesses are a significant public health concern worldwide. These diseases are transmitted to humans through the bites of infected mosquitoes. Some of the most common mosquito-borne illnesses include malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus, chikungunya, and West Nile virus. Each of these diseases presents its own set of symptoms and potential complications, ranging from mild flu-like symptoms to severe and sometimes fatal outcomes. Prevention and control of these illnesses are essential to reduce the global burden of mosquito-borne diseases.
Importance of Mosquito Control
Effective mosquito control measures are critical in preventing the spread of mosquito-borne diseases. These measures include eliminating standing water where mosquitoes breed, using insect repellent, wearing protective clothing, and implementing mosquito control programs. By reducing mosquito populations and minimizing human-mosquito contact, the risk of disease transmission can be significantly reduced. Public health education on the importance of mosquito control and community involvement are also key components in combating these diseases. Investing in mosquito control not only protects individual health but also contributes to overall community well-being and safety.
Malaria
Malaria, a well-known mosquito-borne disease, is caused by the Plasmodium parasite transmitted through the bites of infected Anopheles mosquitoes. The symptoms of malaria can range from mild to severe and may include fever, chills, sweating, body aches, and in severe cases, organ failure and death. It is essential to diagnose and treat malaria promptly to prevent complications and fatalities.
Transmission and Symptoms
The transmission of malaria occurs when infected female Anopheles mosquitoes bite humans to feed on blood. Once the parasites enter the bloodstream, they travel to the liver and multiply, leading to the typical cycle of symptoms associated with malaria. Early symptoms may mimic the flu, making diagnosis challenging without proper testing.
Prevention and Treatment
Prevention of malaria involves avoiding mosquito bites by using insect repellent, sleeping under insecticide-treated bed nets, and taking antimalarial medications when traveling to at-risk areas. Effective treatment usually includes antimalarial drugs to eliminate the parasites from the body. Timely intervention and continuous efforts in prevention are crucial in the fight against this deadly disease.
Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is a viral infection transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes, known for its debilitating symptoms. The signs and symptoms of dengue fever often include sudden onset high fever, severe headaches, joint and muscle pain, rashes, and in severe cases, hemorrhagic fever leading to shock and even death. Early detection and prompt medical care are essential in managing dengue fever to prevent complications.
Signs and Symptoms:
The hallmark symptom of dengue fever is a high fever, which is accompanied by severe headaches, pain behind the eyes, muscle, and joint pain, a characteristic skin rash, and in severe cases, bleeding manifested as nosebleeds or easy bruising. If experiencing these symptoms, seeking medical attention promptly is crucial for proper diagnosis and management.
Management and Prevention:
Treatment for dengue fever focuses on managing symptoms, staying hydrated, and avoiding non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that can worsen bleeding. Prevention methods include using mosquito repellents, wearing protective clothing, and eliminating breeding sites like stagnant water around homes. Public health education is essential in raising awareness and preventing the spread of dengue fever.
Zika Virus
Zika virus, similar to dengue fever, is primarily transmitted through the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes. The disease characteristics of Zika virus include symptoms like fever, rash, joint pain, and red eyes. While most cases of Zika virus are mild with symptoms lasting for several days to a week, the virus poses a significant concern for pregnant women due to its association with birth defects, particularly microcephaly.
Disease Characteristics:
Zika virus infections often present with mild symptoms such as fever, rash, joint pain, and red eyes. In some cases, individuals may not show any symptoms at all. The disease typically runs its course within a week, with rest, hydration, and symptomatic treatment recommended.
Impact on Pregnant Women:
For pregnant women, contracting Zika virus poses a severe risk to the unborn child. The virus has been linked to birth defects, particularly microcephaly, where babies are born with unusually small heads and underdeveloped brains. Pregnant women are advised to take precautions to prevent mosquito bites and seek medical advice if they suspect Zika virus infection during pregnancy. Public health efforts play a critical role in raising awareness about the risks associated with Zika virus and promoting preventive measures.
Also Read: Learn About Polio Disease: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention
West Nile Virus
Symptoms and Complications
The West Nile Virus, transmitted by infected mosquitoes, can lead to various symptoms and potential complications. Symptoms commonly include fever, headache, body aches, skin rash, and swollen lymph nodes. In severe cases, individuals may experience more serious complications such as inflammation of the brain (encephalitis) or inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord (meningitis). It is essential to monitor any symptoms and seek medical attention if needed.Preventive measures are crucial in reducing the risk of West Nile Virus infections.
Prevention Methods
Prevention methods include eliminating stagnant water sources where mosquitoes breed, wearing long sleeves and pants when outdoors, applying insect repellent containing DEET, and installing window screens to keep mosquitoes outside. Public health authorities often conduct mosquito control programs to minimize the spread of the virus and educate the public on preventive actions to take.Being proactive in preventing mosquito bites and staying informed about the West Nile Virus are key steps in safeguarding against this potentially harmful disease.
