Overview of Endometriosis
Definition and Symptoms
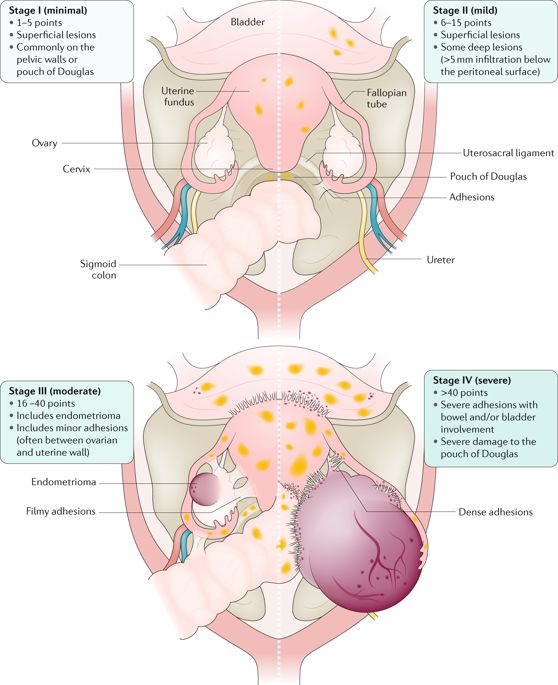
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus, known as endometrium, begins to grow outside of the uterus. This can lead to severe pelvic pain, especially during menstruation. Other common symptoms include heavy menstrual bleeding, pain during intercourse, and infertility. It is essential to consult a healthcare provider if you experience these symptoms.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of endometriosis is not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to its development. These include hormonal imbalances, genetics, and retrograde menstruation, where menstrual blood flows back into the pelvic cavity instead of leaving the body. Risk factors for endometriosis include a family history of the condition, starting menstruation at an early age, and never giving birth. It is crucial to raise awareness about this condition to encourage early diagnosis and appropriate management.
Diagnosis of Endometriosis
In diagnosing endometriosis, healthcare providers typically begin by taking a detailed medical history and performing a physical examination. During the physical exam, they may check for any palpable abnormalities or signs of the condition. Medical history can provide insights into symptoms experienced and help in establishing a preliminary diagnosis.
Medical History and Physical Exam
Further diagnostic tests may be recommended to confirm the presence of endometriosis. Imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI can help visualize any abnormal growths or lesions in the pelvic region. However, the gold standard for diagnosing endometriosis is through laparoscopy, a minimally invasive surgical procedure. During laparoscopy, a thin, lighted tube with a camera is inserted into the abdomen to allow the healthcare provider to view and potentially remove any endometrial tissue growths for biopsy.
Imaging Tests and Laparoscopy
By combining medical history, physical examination, imaging tests, and laparoscopy, healthcare providers can accurately diagnose endometriosis, enabling appropriate treatment and management strategies tailored to the individual’s needs. Early diagnosis is crucial in effectively managing endometriosis and alleviating symptoms.
Treatment Options for Endometriosis
In the journey to manage endometriosis, treatment options play a crucial role in providing relief and improving quality of life for individuals affected by this condition. The primary aim of treatment is to alleviate symptoms, reduce pain, and prevent the progression of the disease. Healthcare providers may recommend a combination of approaches tailored to the severity of the symptoms and the individual’s overall health.
Medications
Medications are often the first line of treatment for managing endometriosis. Pain relievers such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help alleviate the pelvic pain and cramping associated with the condition. Hormonal therapies, including birth control pills, progestin therapy, and gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, aim to suppress the menstrual cycle, reduce pain, and slow the growth of endometrial tissue.
Surgery
In cases where medications alone are ineffective or for severe endometriosis, surgical intervention may be recommended. Laparoscopic surgery, similar to the diagnostic procedure, can be utilized to remove endometrial tissue growths, scar tissue, and adhesions. In more severe cases, a hysterectomy may be considered as a last resort to remove the uterus and potentially the ovaries. However, surgery is typically reserved for cases where other treatment options have been ineffective in managing symptoms. Consulting with a healthcare provider to discuss the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual needs is crucial for effectively managing endometriosis.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Endometriosis
Diet and Nutrition
Implementing changes in diet and nutrition can have a positive impact on managing endometriosis. Some women find relief by avoiding inflammatory foods such as processed foods, sugary snacks, and high-fat red meats. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and Omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation and manage symptoms. Maintaining a well-balanced diet rich in nutrients can support overall health and potentially alleviate endometriosis symptoms.
Exercise and Stress Management
Regular exercise and stress management techniques can also play a crucial role in managing endometriosis. Engaging in physical activities such as yoga, walking, or swimming can help reduce stress levels and alleviate pain. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural pain relievers and mood boosters. Additionally, practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or mindfulness can help reduce stress and promote overall well-being. Combining regular exercise with stress management strategies can contribute to a more holistic approach to managing endometriosis and improving quality of life.
Also Read: AAV Adeno: Understanding the Adeno-Associated Virus Vector
Impact of Endometriosis on Fertility
Infertility and Endometriosis
Endometriosis can have a significant impact on fertility for women trying to conceive. The condition can lead to issues such as ovarian cysts, adhesions, and inflammation, which may affect the reproductive organs’ function. In severe cases, endometriosis can cause scar tissue formation, blocking the fallopian tubes, and hindering the egg’s travel to the uterus for fertilization. This can result in difficulty getting pregnant naturally and an increased risk of infertility.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies
For individuals facing infertility due to endometriosis, assisted reproductive technologies (ART) can offer viable solutions. Techniques such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), intrauterine insemination (IUI), or egg freezing may be recommended to help overcome fertility challenges associated with endometriosis. These advanced reproductive options provide opportunities for individuals with endometriosis to fulfill their dreams of starting or expanding their families. It is essential to consult with fertility specialists to explore the most suitable ART options based on individual circumstances and health factors.
