Overview of ALS Disease
Understanding Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
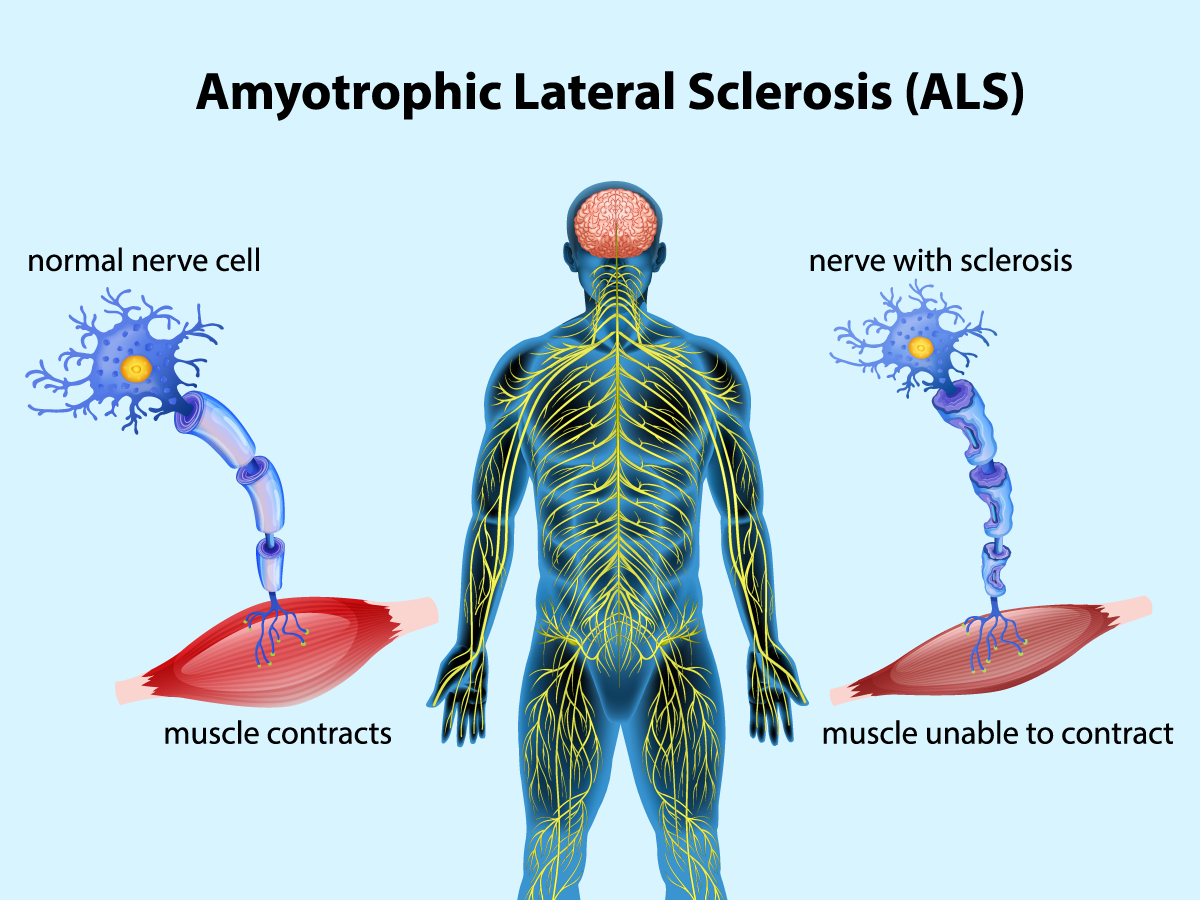
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, commonly known as ALS or Lou Gehrig’s disease, is a progressive neurological disorder that affects nerve cells in the brain and the spinal cord. This degenerative condition leads to the gradual deterioration of voluntary muscle movement, eventually causing paralysis. Individuals with ALS may experience muscle weakness, twitching, and difficulty speaking, swallowing, and breathing as the disease advances. The exact cause of ALS remains unknown, although genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role in its development. Currently, there is no cure for ALS, and treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving the quality of life for patients.
Historical Background of ALS
ALS was first discovered in the 19th century by the French neurologist Jean-Martin Charcot, who identified and described the key symptoms of the disease. Over the years, significant progress has been made in understanding ALS, but much about this complex condition remains a mystery. The ALS Ice Bucket Challenge in 2014 brought global attention to the disease, raising funds for research and increasing awareness about the challenges faced by ALS patients. As researchers continue to investigate potential treatments and causes of ALS, efforts are ongoing to support patients and their families in coping with this debilitating illness.
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic Factors Associated with ALS | Environmental Triggers Linked to ALS
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is a complex disease that involves various genetic and environmental factors. Genetic predisposition plays a crucial role in the development of ALS. Mutations in specific genes, such as C9orf72, SOD1, and FUS, have been identified as contributing factors to the disease. These genetic abnormalities affect nerve cells’ functioning, leading to the progressive degeneration seen in ALS patients.On the other hand, environmental triggers have also been implicated in ALS. Exposure to certain toxins and chemicals, such as lead, pesticides, and heavy metals, may increase the risk of developing ALS. Additionally, viral infections, traumatic injuries, and lifestyle factors like smoking and intense physical activity have been suggested as potential environmental triggers for the disease.Understanding the interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental influences is vital in unraveling the complexities of ALS. Research efforts continue to focus on identifying the underlying causes of ALS to develop effective treatment strategies and, ultimately, find a cure for this debilitating condition.
Symptoms and Progression
Early Signs and Symptoms of ALS | Progression Stages of the Disease
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) manifests through a range of symptoms and follows a distinct progression pattern. Early signs of ALS often include muscle weakness, twitching, and cramping, particularly in the arms and legs. Patients may also experience difficulties with speaking, swallowing, or breathing as the disease progresses.As ALS advances, it typically moves through specific stages marked by increased muscle deterioration and loss of function. The initial stage may involve weakness in a specific muscle group, which then spreads to other areas of the body. Subsequent stages see a decline in mobility, leading to challenges in performing daily activities independently.Understanding the symptoms and progression of ALS is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management of the disease. By recognizing the signs early on and monitoring the progression stages, healthcare professionals can provide patients with appropriate care and support to enhance their quality of life. Ongoing research endeavors aim to further elucidate the disease’s course and develop innovative treatments to improve patient outcomes and slow ALS progression.
Diagnosis and Screening
Tests Used for Diagnosing ALS | Importance of Early Detection
Blog Section:When it comes to diagnosing Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), healthcare professionals may utilize various tests to confirm the presence of the disease. Common diagnostic tools include electromyography (EMG), nerve conduction studies, blood tests, imaging scans like MRI or CT scans, and muscle biopsies. These tests help physicians assess nerve and muscle function, eliminate other potential conditions with similar symptoms, and ultimately reach a conclusive ALS diagnosis.Early detection of ALS is vital for several reasons. By identifying the disease in its initial stages, patients can receive timely and appropriate medical interventions, symptom management strategies, and supportive care. Diagnosing ALS early also enables individuals to make informed decisions regarding their treatment options and future plans. Moreover, early detection may provide researchers with valuable insights into the disease’s progression, potentially leading to more effective therapies and management strategies.In conclusion, timely diagnosis through the use of various screening tests is crucial for individuals suspected of having ALS. Early detection not only aids in providing optimal care and support but also plays a significant role in advancing research efforts aimed at improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Also Read: Understanding Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Causes,…
Treatment Options
Medications and Therapies for ALS | Alternative and Complementary Treatments
Blog Section:When it comes to addressing Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), healthcare providers offer a range of treatment options tailored to manage symptoms and enhance the quality of life for patients. Medications such as Riluzole and Edaravone are commonly prescribed to slow the progression of the disease and alleviate symptoms. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy play pivotal roles in maintaining muscle function, mobility, and communication abilities.Alternative and complementary treatments, such as acupuncture, massage therapy, and nutritional supplements, are also explored by some patients to alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being. While these methods may not cure ALS, they can offer additional relief and support alongside conventional treatments.It is crucial for individuals diagnosed with ALS to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses their unique needs and goals. By combining traditional medications with alternative therapies, patients can optimize their care and potentially enhance their quality of life despite the challenges posed by ALS.
