Overview of Hepatitis
What is Hepatitis?
Hepatitis is characterized as an inflammation of the liver, commonly caused by a viral infection. It can also result from other factors such as excessive alcohol consumption, medications, toxins, and autoimmune diseases. The condition can be acute, lasting only a few weeks, or chronic, enduring for a lifetime. Hepatitis represents a significant global health issue, with millions of individuals affected each year.
Types of Hepatitis
There are several types of hepatitis, including Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E.
- Hepatitis A is usually transmitted through contaminated food or water.
- Hepatitis B spreads through contact with infectious body fluids.
- Hepatitis C is commonly transmitted through blood-to-blood contact.
- Hepatitis D only occurs in individuals who are infected with the Hepatitis B virus.
- Hepatitis E usually results from consuming contaminated water.
Each type of hepatitis varies in terms of severity, transmission methods, and available treatments. It is crucial to understand the differences to prevent, diagnose, and manage the condition effectively.
Understanding Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is a viral liver disease caused by the Hepatitis A virus (HAV). The most common mode of transmission is through consuming contaminated food or water. Poor sanitation and inadequate hygiene practices contribute to the spread of the virus, especially in areas with limited access to clean water. The virus can also be transmitted through close personal contact or consuming food prepared by an infected individual. Hepatitis A is highly contagious, making it crucial to practice proper hygiene and get vaccinated to prevent the disease.
Causes and Transmission
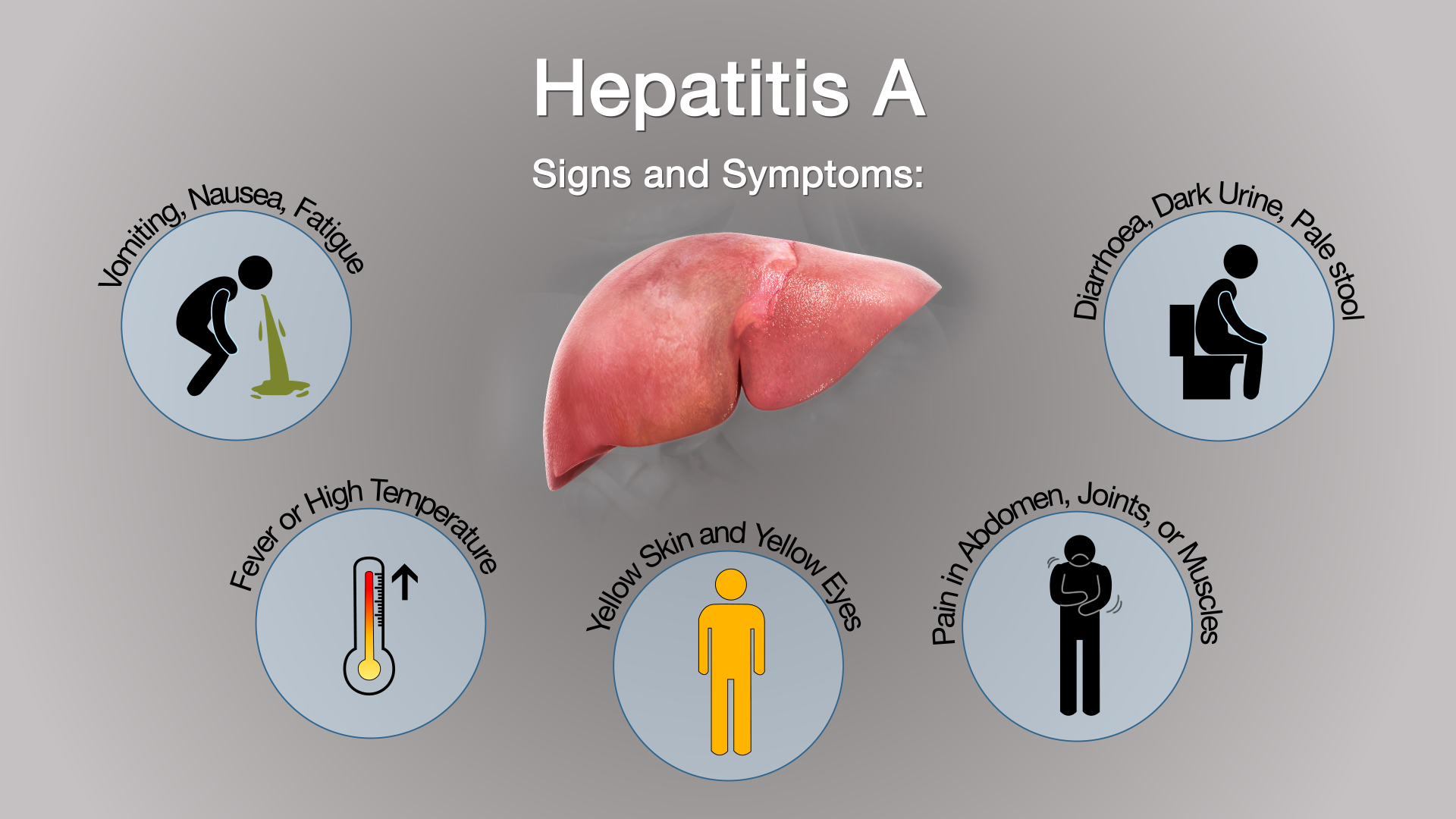
The primary cause of Hepatitis A is the ingestion of the virus through contaminated food or water. The virus can also spread through close contact with an infected person or by consuming food prepared by someone with the virus. Symptoms typically appear within 2 to 6 weeks after exposure and may include fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, jaundice, and dark urine. Diagnosis is confirmed through blood tests that detect specific antibodies produced by the body in response to the virus.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of Hepatitis A may vary from mild to severe and can last for a few weeks to several months. Early diagnosis is essential to prevent complications and further transmission of the virus. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and rest, as Hepatitis A does not have a specific antiviral treatment. Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent Hepatitis A, especially for individuals traveling to regions with high infection rates or during outbreaks. Regular handwashing, safe food practices, and maintaining good personal hygiene are also key preventive measures against Hepatitis A.
Prevention of Hepatitis A
Vaccination
Vaccination is the most effective method to prevent Hepatitis A. Getting vaccinated creates immunity against the virus, reducing the risk of infection. It is particularly important for individuals traveling to areas with high Hepatitis A prevalence or during outbreaks. By ensuring you are up to date with your vaccinations, you can protect yourself and others from this contagious liver disease.
Hygiene and Sanitation Practices
Practicing good hygiene and sanitation is crucial in preventing the spread of Hepatitis A. Regular handwashing with soap and water, especially after using the restroom and before handling food, can help eliminate the virus. Safe food practices, such as washing fruits and vegetables thoroughly and avoiding consuming undercooked foods, are essential steps in reducing the risk of contamination. Additionally, maintaining clean and sanitary living environments can prevent the transmission of the virus, especially in crowded or communal settings. By implementing these practices, you can significantly lower the chances of contracting Hepatitis A and contribute to overall public health.
Treatment for Hepatitis A
Medical Interventions
When it comes to treating Hepatitis A, there are limited medical interventions available. Typically, healthcare providers recommend rest, adequate hydration, and a healthy diet to support the body’s recovery. In some cases, antiviral medications may be prescribed, but these are not standard treatments for Hepatitis A. Monitoring liver function and overall health is essential during the recovery process to ensure proper healing and to manage any complications that may arise.
Home Care and Support
At home, individuals diagnosed with Hepatitis A can aid their recovery by getting plenty of rest, staying hydrated, and consuming nutritious meals. Avoiding alcohol and certain medications that can stress the liver is crucial during this time. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any new medications to prevent adverse effects on the liver. Additionally, having a strong support system of family and friends can provide emotional support during the recovery period, which is vital for overall well-being. Patience and self-care are key components of managing Hepatitis A at home.
Also Read: Understanding Viral Infection Infection: Causes, Symptoms,..
Complications of Hepatitis A
Liver Damage
In some cases, Hepatitis A can lead to liver damage. While most individuals recover fully without long-term liver issues, there is a risk of complications, especially in severe cases. Monitoring liver function through blood tests is vital to assess any damage and ensure proper treatment if needed.
Long-Term Effects
Although rare, Hepatitis A can sometimes result in long-term effects on the body. These effects may include ongoing liver problems, fatigue, and general feelings of unwellness. It is essential for individuals who have had Hepatitis A to attend follow-up appointments with healthcare providers to monitor for any lingering issues and address them promptly. By staying vigilant and proactive, potential long-term effects can be managed effectively to promote overall health and well-being. Regular health check-ups and maintaining a healthy lifestyle play a crucial role in preventing and managing any long-term complications related to Hepatitis A.
